(Covers benefits, real-world examples, DMAIC explained, and more.)
SSGI Lean Six Sigma Training Trusted by professionals working at:
Welcome to our Lean Six Sigma guide. In this resource, we’ll break down what Lean Six Sigma is, why it’s the most effective methodology for process improvement, and how certification can benefit your career and organization.
✅ Quick Summary:
Lean Six Sigma is the most widely adopted methodology for improving efficiency and quality in business operations. This guide explains what Lean Six Sigma is, how it works (DMAIC), who uses it, and why certification is a smart investment in 2025.
- • What is Lean Six Sigma?
- • What is Lean?
- • What is Six Sigma?
- • Lean vs Six Sigma
- • Combining Lean and Six Sigma
- • History of Lean Six Sigma
- • DMAIC Example
- • The Role of Kaizen in Lean Six Sigma
- • Lean Six Sigma Principals
- • Lean Six Sigma Tools
- • Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
- • Industries that use Lean Six Sigma
- • Is Lean Six Sigma Worth It?
- • What Are the Lean Six Sigma Belt Levels?
- • How to Choose a Lean Six Sigma Certification
- • Why Should You Consider Lean Six Sigma Certification?
- • Salary Information
- • Lean Six Sigma Project Examples
- • Organizational Development and Lean Six Sigma
- • Lean Six Sigma Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Lean Six Sigma? Definition, Benefits & How It Works [2025]
Lean Six Sigma is a structured methodology that combines Lean’s focus on speed and waste reduction with Six Sigma’s focus on quality and variation control. It uses data-driven tools and the DMAIC framework to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction across industries.
Are you looking to improve operations, eliminate waste, and enhance quality, all while advancing your career? Lean Six Sigma training and certification combine two proven methodologies into one powerful framework for driving efficiency and performance in any industry.
At its core, Lean Six Sigma merges Lean’s focus on speed and waste reduction with Six Sigma’s emphasis on quality and consistency. The result is a data-driven, structured approach that helps organizations streamline processes, reduce variation, and deliver greater value to customers.
Lean Six Sigma is trusted by leading companies, government agencies, and institutions worldwide for its ability to achieve measurable results, whether through cutting costs, improving service delivery, or increasing customer satisfaction. It also opens doors to new career opportunities, higher pay, and leadership potential for professionals across industries.
Because it addresses both efficiency and quality, Lean Six Sigma has become the most widely adopted improvement methodology across sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing, government, education, and technology.
Watch: What Is Lean Six Sigma?
In this short video, Professor Barry Shore explains how Lean Six Sigma integrates efficiency and quality improvement to drive organizational excellence.
Whether you’re just getting started or looking to strengthen your process improvement skills for leadership, Lean Six Sigma offers a practical, results-driven approach to achieving operational excellence.
Lean is a methodology focused on eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and delivering more value with fewer resources. It emphasizes speed, flow, and customer value.
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that uses statistical tools to reduce variation and defects in processes, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology focused on reducing variation and defects in processes, ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
Lean vs Six Sigma: What’s the Difference?
Lean focuses on removing waste and improving process speed, while Six Sigma aims to reduce variation and improve quality. Together, they form a powerful framework for efficiency and excellence. For a detailed comparison, visit our full guide on the difference between Lean and Six Sigma .
While both Lean and Six Sigma are methodologies aimed at improving business performance, Lean vs Six Sigma take different approaches. Lean methodology is centered around increasing process speed, eliminating waste, and delivering value to the customer as efficiently as possible. It focuses on streamlining workflows, reducing delays, and simplifying operations.
Six Sigma, on the other hand, is a data-driven methodology focused on reducing process variation, improving consistency, and achieving near-perfect quality. It uses statistical tools to identify the root causes of defects and applies rigorous problem-solving techniques to eliminate them.
Although they began as separate methodologies, many organizations now combine them under the umbrella of Lean Six Sigma to drive both speed and quality improvements in a single, unified approach.
Lean vs Six Sigma: Side-by-Side Comparison
While Lean and Six Sigma share the goal of process improvement, they approach it from different angles. Here’s a quick comparison to help you understand how each method contributes to operational excellence.
| Feature | Lean | Six Sigma |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Eliminate waste, speed up processes | Reduce defects and variation |
| Tools | 5S, Value Stream Mapping, Kaizen | DMAIC, Control Charts, FMEA |
| Approach | Visual, process-based | Data-driven, statistical |
| Goal | Efficiency & flow | Quality & consistency |
Combining Lean and Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma combines the strengths of Lean and Six Sigma to improve speed, reduce waste, and enhance quality. It’s a comprehensive framework for continuous improvement.
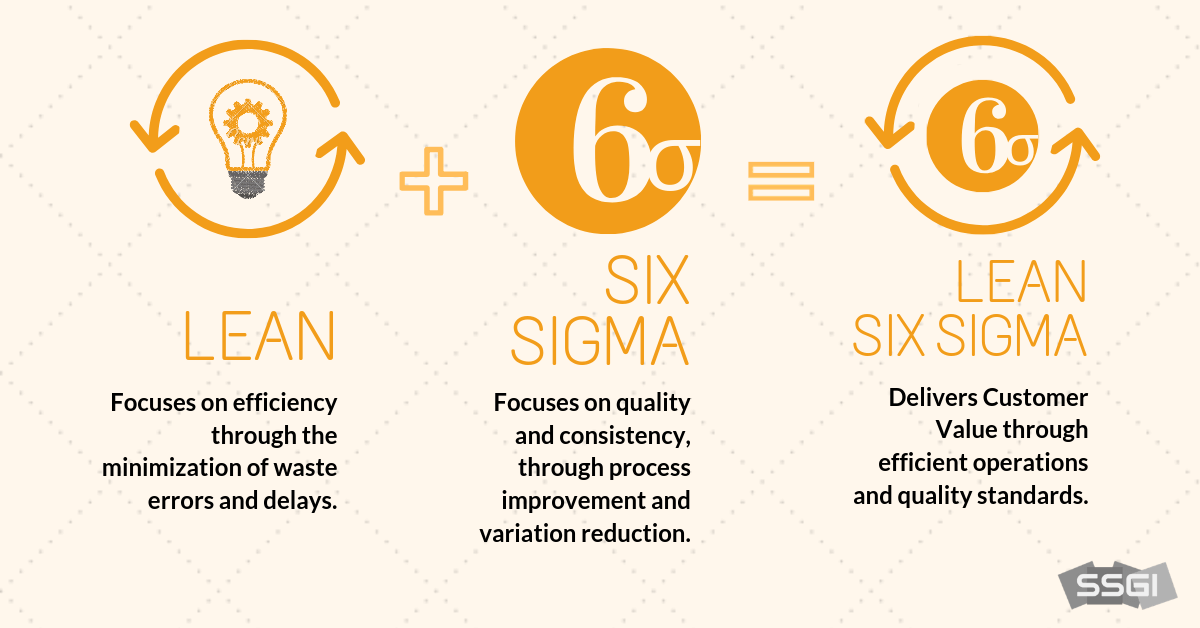
Combining Lean and Six Sigma into Lean Six Sigma creates a powerful approach to enhancing processes and achieving operational excellence. The methodology merges the strengths of both Lean and Six Sigma to create a comprehensive framework that addresses efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
History and Evolution of Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma evolved from Toyota’s Lean principles and Motorola’s Six Sigma methods. It became widely adopted by companies seeking both quality and efficiency.
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that combines the principles of Lean manufacturing and Six Sigma to improve efficiency and quality. It was developed in the late 20th century, drawing from the quality control methods pioneered by Motorola and the lean manufacturing techniques developed by Toyota. Key figures like Bill Smith and Mikel Harry played pivotal roles in its evolution, leading to widespread adoption across various industries.

Several decades ago, at Motorola Corporation expressed concern that traditional methods of quality assurance were not enough to assure quality. Under his guidance, Motorola developed the methodology and cultural changes necessary to deploy a Six Sigma program that would change the way modern organizations deliver and manage quality control. The program was so successful that Motorola documented more than $16 Billion in savings from this new approach.
Since then, countless companies from manufacturing to health care have adopted Six Sigma. The most notable spokesperson for this discipline has been Jack Welch who implemented this program at General Electric in 1995.
 Lean began in the automobile industry and dates back to the innovations in mass production introduced by Henry Ford. Utilizing interchangeable parts and moving conveyors, the concept of efficient process flow was born. The only shortcoming was Ford’s inability to deliver variety. You could order any color Ford as long as it was black!
Lean began in the automobile industry and dates back to the innovations in mass production introduced by Henry Ford. Utilizing interchangeable parts and moving conveyors, the concept of efficient process flow was born. The only shortcoming was Ford’s inability to deliver variety. You could order any color Ford as long as it was black!
How to Use Lean Six Sigma (DMAIC Explained)
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It’s the core framework used in Lean Six Sigma to identify problems, implement solutions, and sustain improvements over time.

DEFINE
The Role of Kaizen in Lean Six Sigma
Kaizen means "continuous improvement" in Japanese. It’s a core principle of Lean that focuses on small, incremental changes that add up to major improvements over time.
What is Kaizen?
Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning “continuous improvement,” is a key component of Lean methodology. It focuses on making small, incremental changes to enhance efficiency and quality within processes.
Principles of Kaizen
Continuous Improvement
Emphasizes making ongoing, small improvements rather than large-scale changes.
Employee Involvement
Encourages participation from all employees, from management to frontline workers, to suggest process improvements.
Elimination of Waste
Aims to identify and remove activities that do not add value to the process.
How Kaizen Works in Lean Six Sigma
Kaizen plays a crucial role in Lean Six Sigma by:
☑️ Identifying Opportunities: Regularly reviewing processes to identify inefficiencies.
☑️ Implementing Changes: Making small, manageable changes to improve processes.
☑️ Sustaining Improvements: Standardizing successful changes to maintain improvements over time.
Benefits of Kaizen in Lean Six Sigma
Kaizen empowers teams to identify small, incremental changes that lead to significant long-term gains. By integrating Kaizen into Lean Six Sigma projects, organizations foster a culture of collaboration, data-driven decision-making, and sustained performance improvement.
Employee Engagement
Involving employees in improvement initiatives increases their engagement and morale.
Enhanced Quality
Continuous improvements help maintain high-quality standards and reduce defects.
Improved Efficiency
Streamlined processes reduce waste and increase operational efficiency.
Lean Six Sigma Principals
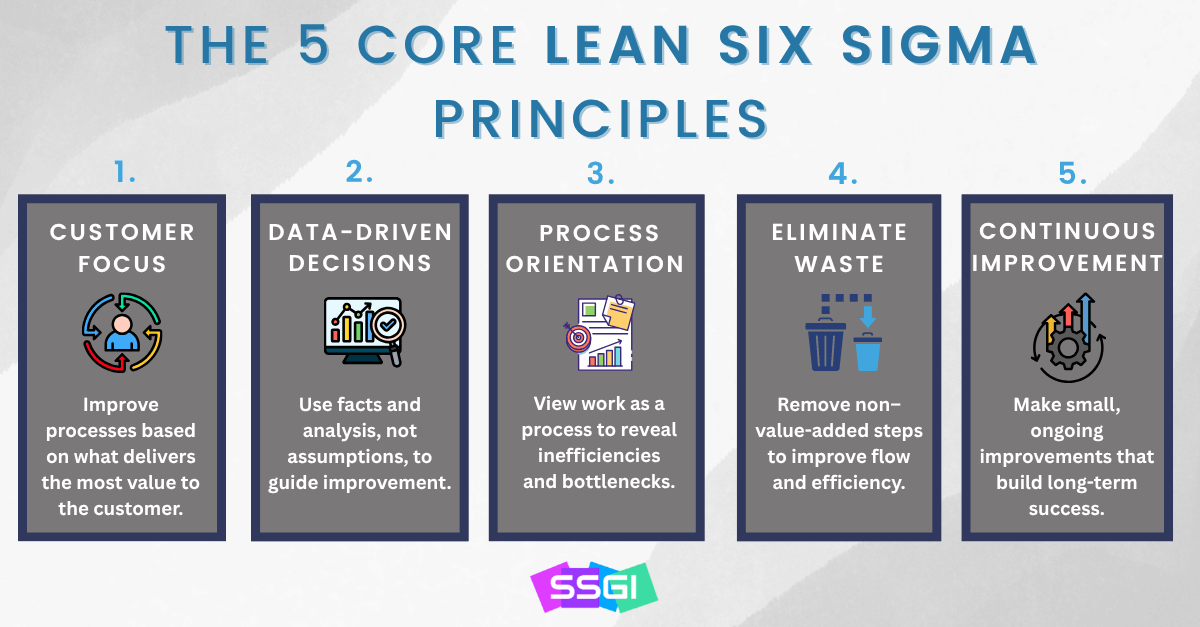 Lean Six Sigma is built on a foundation of core principles that drive continuous improvement and operational excellence across all industries. These principles combine data-driven decision-making with a focus on customer value and waste reduction.
Lean Six Sigma is built on a foundation of core principles that drive continuous improvement and operational excellence across all industries. These principles combine data-driven decision-making with a focus on customer value and waste reduction.
- Customer Focus: Every process improvement begins with understanding and enhancing customer value.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Use facts and analysis—not assumptions—to identify root causes and guide improvement.
- Process Orientation: View work as a process, not isolated tasks, to reveal inefficiencies and opportunities.
- Elimination of Waste: Reduce non-value-added steps to improve flow and efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement: Empower teams to make ongoing, incremental improvements that lead to long-term success.
Lean Six Sigma projects rely on practical tools that turn data into action. Popular methods include the Pareto Chart for prioritizing key problems, the 5 Whys for root cause analysis, Value Stream Mapping to visualize processes, and the DMAIC framework to drive improvement from definition to control. Explore detailed examples of these tools below.
Lean Six Sigma Tools and Techniques
Lean Six Sigma professionals use a variety of analytical and process-improvement tools to identify waste, eliminate variation, and sustain measurable results. These tools form the foundation of every improvement project and help teams make data-driven decisions that lead to lasting efficiency.
Tools like 5S, SIPOC, Value Stream Mapping, Control Charts, and Pareto Charts are commonly used to improve processes and eliminate inefficiencies in Lean Six Sigma projects.
Let’s explore some of the tools and techniques utilized in Lean Six Sigma (LSS). During our training programs, we focus on improving actual processes within the organization. Participants engage in real-world projects and gain hands-on experience, witnessing firsthand the positive impact of each successful LSS initiative.
Several tools are commonly used in Lean Six Sigma process improvement to analyze, measure, and enhance processes. The popularity of these tools can vary based on the specific needs of a project, but some widely used ones include:
5S for workplace organization:
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
Streamlined operations, reduced waste, improved quality, increased customer satisfaction, and better decision-making. It benefits individuals and organizations alike — across all industries.

Embracing Lean Six Sigma brings a multitude of benefits to organizations seeking to enhance efficiency and elevate overall performance.
One of the key advantages lies in the methodology’s ability to streamline processes, leading to increased operational efficiency and reduced resource wastage. This, in turn, contributes to substantial cost savings, making Lean Six Sigma a powerful tool for improving financial performance. Whether a Fortune 500 enterprise or a small business, the implementation of Lean Six Sigma principles lays the groundwork for sustainable growth, superior quality, and lasting success.
Benefits of Using Lean Six Sigma
These benefits highlight why Lean Six Sigma is one of the most adopted methodologies in process improvement today. By combining speed with precision, organizations can transform their operations, empower employees, and deliver better outcomes for customers. Whether you’re looking to reduce costs, improve service delivery, or build a culture of continuous improvement, Lean Six Sigma offers a structured yet flexible framework to get there. It’s not just a toolkit—it’s a mindset shift that drives lasting results.
Enhanced Efficiency
Streamlining processes leads to increased efficiency, reducing the time and resources required to deliver products or services.
Quality Improvement
Rigorous problem-solving techniques and statistical analysis result in a significant reduction in defects, ensuring higher-quality outcomes.
Cost Reduction
By eliminating waste and optimizing resources, Lean Six Sigma contributes to cost reduction and improved financial performance.
Cultural Transformation
The methodology often leads to a cultural transformation within organizations, instilling a mindset of continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making.
Customer Satisfaction
The ultimate goal is to deliver more value to customers, meeting and exceeding their expectations consistently.
Synergistic Approach
Combining Lean and Six Sigma creates a synergistic effect, addressing both efficiency and quality aspects concurrently.
Comprehensive Problem-Solving
Lean Six Sigma provides a comprehensive toolkit for problem-solving, incorporating Lean’s waste reduction and Six Sigma’s variation reduction methodologies.
Versatility
Lean Six Sigma is adaptable to various industries and sectors, making it a versatile approach for organizations seeking improvement in diverse operational contexts.
Who Benefits from Lean Six Sigma?
- Skill Development: Gain valuable skills in problem-solving, data analysis, and process improvement.
- Engagement: Active participation in projects boosts job satisfaction and ownership.
- Improved Quality: Reduction in defects and errors leads to higher-quality products and services.
- Faster Delivery: Optimized processes result in quicker delivery and service.
- Strategic Alignment: Aligns improvement efforts with key business objectives.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Leverages analytics for smarter, more informed leadership decisions.
Now that we’ve explored what Lean Six Sigma is and how it differs from traditional Six Sigma, let’s take a closer look at the core principles and tools that drive its success in organizations worldwide.
Industries That Use Lean Six Sigma
Organizations of all sizes—from Fortune 500 companies to hospitals, banks, and universities—use Lean Six Sigma to optimize performance. It’s applied in manufacturing, healthcare, government, education, and more.
Lean Six Sigma is versatile and applicable across diverse industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, service, and more. Organizations of all sizes, from Fortune 500 companies to small businesses, have successfully implemented Lean Six Sigma principles to drive continuous improvement.
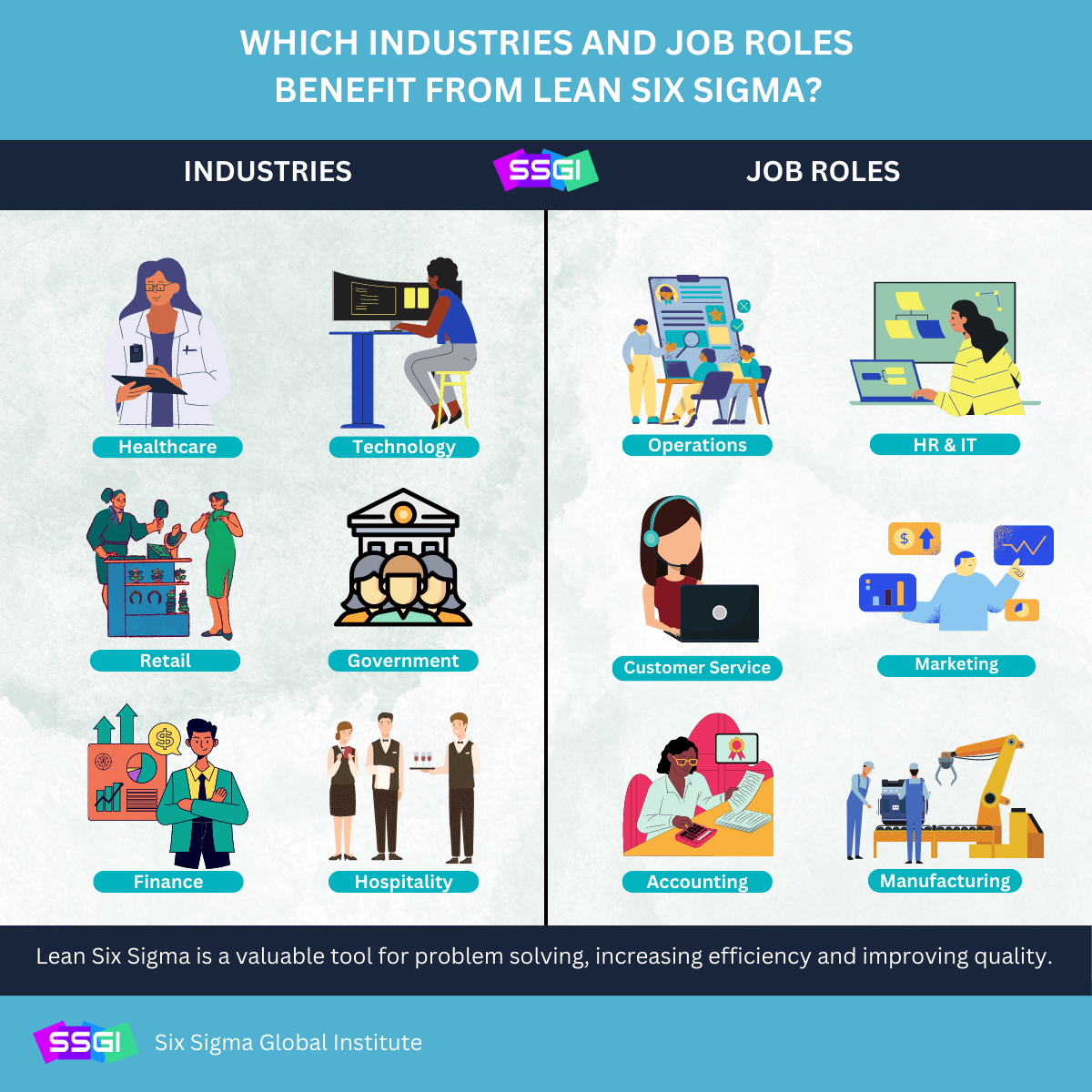
Industries that benefit from Lean Six Sigma include:
Manufacturing: Improve production processes, reduce waste, and enhance product quality.
Healthcare: Streamline patient care, reduce wait times, and minimize medical errors.
Finance: Improve compliance, reduce transaction errors, and optimize workflows.
Information Technology (IT): Enhance software development lifecycles, improve incident management, and reduce system downtime.
Logistics & Supply Chain: Optimize distribution, reduce lead times, and lower transportation costs.
Government & Public Sector: Improve service delivery, reduce bureaucracy, and enhance public satisfaction.
Higher Education & Nonprofits: Streamline operations, reduce overhead, and increase program efficiency.
Is Lean Six Sigma Worth it?
For professionals, it’s one of the most valuable career credentials you can earn. It boosts your salary potential, sharpens your problem-solving skills, and opens doors to leadership and continuous improvement roles. For organizations, it delivers measurable results — greater efficiency, fewer defects, and millions in cost savings each year.


Why It’s Worth It for Professionals
Higher earnings: According to ASQ’s salary surveys, certified professionals earn significantly more than non-certified peers.
Career advancement: Lean Six Sigma credentials are recognized across industries — from healthcare and government to manufacturing and tech.
Stronger skill set: You’ll master proven tools like DMAIC, SIPOC, and Value Stream Mapping that apply to nearly any business challenge.
Credibility and leadership: Certification signals that you can lead teams, manage change, and drive measurable results.
Why It’s Worth It for Organizations
Efficiency gains: Lean methods eliminate waste, streamline operations, and increase throughput.
Quality improvement: Six Sigma tools reduce errors and rework, improving consistency and customer satisfaction.
Lower costs: Organizations using Lean Six Sigma regularly report project ROIs of 3–10× through waste reduction and process optimization.
Sustainable improvement culture: Teams adopt a structured, data-driven approach that encourages collaboration and long-term success.
Real-World Proof
Across sectors, companies use Lean Six Sigma to achieve tangible results:
Healthcare: Reduced patient wait times and improved discharge efficiency.
Manufacturing: Lower defect rates and production costs.
Technology & Services: Faster onboarding, fewer customer escalations, and stronger quality control.
Quick fact: Most SSGI-certified professionals complete their first successful Lean Six Sigma project within 30–90 days of starting their training.
If you’re looking for a clear, proven way to strengthen your resume, improve your performance, and deliver measurable results at work, Lean Six Sigma certification is absolutely worth it.
👉 Want a deeper look at the career, salary, and certification ROI? Read our full guide: Is Six Sigma Worth It?
What Are the Lean Six Sigma Belt Levels?
White, Yellow, Green, Black, and Master Black Belt levels reflect increasing levels of expertise — from foundational knowledge to advanced leadership and project coaching roles.

How to Choose a Lean Six Sigma Certification
Look for a program developed by a named expert, with U.S. recognition, flexible access, no renewal fees, and real-world credibility — like those offered by SSGI.
There are many benefits of receiving a Lean Six Sigma certification. Some of the most common include:
The best place to get your six sigma certification is from an industry recognized, accredited and renowned institution. In 2024, several standout providers offer what we see as the top six sigma training courses available. Not all programs are created equal, underscoring the importance of identifying the best six sigma certification institutes, whether pursuing online or in-person training. Below, we delve into 5 of the top six sigma certification programs, aiding you in your quest for the best training program.
Why Should You Consider Lean Six Sigma Certification?
Certification boosts your credibility, opens doors to higher pay and promotions, and proves your ability to lead and improve processes — essential in today’s job market.
Why Get Lean Six Sigma Certified?
Certification boosts your credibility, opens doors to higher pay and promotions, and proves your ability to lead and improve processes — essential in today’s job market.
Lean Six Sigma certification is more than just a professional credential — it’s a strategic investment in your future. Whether you’re aiming to break into a new role, advance within your current company, or lead high-impact projects, this certification signals that you are serious about delivering results.
Here’s why professionals across industries are choosing to get certified:
Demonstrates Mastery: Show employers you have the skills to solve problems, reduce waste, and improve performance.
Enhances Job Security: Certified professionals are often considered indispensable during organizational change or restructuring.
Increases Salary Potential: Certified Lean Six Sigma professionals typically earn more than their non-certified peers.
Boosts Leadership Opportunities: Certification gives you a competitive edge when applying for management or project leadership roles.
Applicable Across Industries: From healthcare and manufacturing to finance and government — Lean Six Sigma skills are in high demand everywhere.
Drives Organizational Impact: Employers want professionals who can make a real impact on the bottom line. Certification gives you that edge.
Whether you’re an entry-level professional or a seasoned leader, Lean Six Sigma certification equips you with the tools, confidence, and credibility to stand out and succeed.
Who Can Benefit from Lean Six Sigma Certification?
Lean Six Sigma is valuable for professionals at every stage of their career — whether you’re entering the workforce, climbing the leadership ladder, or transitioning industries. Here are some common job titles that align well with Lean Six Sigma certification:
| Level | Common Job Titles |
|---|---|
| White Belt | Operations Assistant, Quality Associate, Entry-Level Analyst |
| Yellow Belt | Process Coordinator, Team Lead, Quality Analyst |
| Green Belt | Process Improvement Specialist, Project Manager, Quality Manager |
| Black Belt | Continuous Improvement Manager, Operations Leader, Consultant |
| Master Belt | Director of Process Improvement, VP of Operations, Senior Consultant |
Salary Information for Certified Professionals
Lean Six Sigma certification doesn’t just improve your skills — it can also have a measurable impact on your earning potential. Professionals who earn certifications at higher belt levels consistently report higher average salaries across industries.
According to recent data:
💰 Average Salary by Certification Level
- White Belt: Average salary of $42,000
- Yellow Belt: Average salary of $65,000
- Green Belt: Average salary of $85,000
- Black Belt: Average salary ranging from $95,000 to $110,000
- Master Black Belt: Average salary ranging from $100,000 to $135,000
As organizations continue to prioritize efficiency, quality, and data-driven decision making, the demand for Lean Six Sigma talent is growing, making certification a powerful tool for advancing your career and increasing your income.
👉 For a deeper breakdown of salaries by belt level, industry, and job role, explore our full Six Sigma Salary Guide.
Lean Six Sigma Project Examples
When it comes to understanding how Lean Six Sigma can be implemented in a real world situation, look no further than our Lean Six Sigma project example videos created by Dr. Shore. In these videos Dr. Shore describes through case studies and real world examples how a Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt project and Lean Six Sigma Green Belt project are conducted. Each video aligns to the DMAIC framework.
Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Project Example
This Lean Six Sigma project example is intended for those new to Six Sigma or at the Yellow Belt level.
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Project Example
This is an intermediate level Lean Six Sigma project example for those at the Green Belt level.
Organizational Development and Lean Six Sigma
🌱 CULTURAL ALIGNMENT
Organizational Development: OD focuses on aligning organizational culture with strategic goals, fostering collaboration, and enhancing employee engagement.
Lean Six Sigma: Encourages a culture of continuous improvement, data-driven decision-making, and problem-solving. Employees are empowered to contribute to process optimization.
🔄 CHANGE MANAGEMENT
Organizational Development: Uses strategies to help organizations navigate and adapt to transformations effectively.
Lean Six Sigma: Often requires organizational change. OD-based strategies support successful integration and lasting improvements.
🙌 EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT
Organizational Development: Focuses on creating a positive work environment through employee participation and engagement.
Lean Six Sigma: Empowers employees through involvement in process improvement teams, boosting morale and ownership.
♻️ CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
Organizational Development: Promotes learning and adaptation to external changes through ongoing improvement initiatives.
Lean Six Sigma: Built around continuous improvement through structured, data-driven methods that reduce inefficiencies and defects.
🎯 STRATEGIC ALIGNMENT
Organizational Development: Ensures organizational systems, processes, and culture support long-term goals.
Lean Six Sigma: Aligns projects with strategic priorities, ensuring measurable improvements contribute to success.
📊 DATA-DRIVEN DECISION-MAKING
Organizational Development: Increasingly emphasizes using data to inform organizational changes and improvements.
Lean Six Sigma: Centers around data and statistical tools to guide decision-making and validate results.
Lean Six Sigma Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Lean and Six Sigma?
Lean focuses on eliminating waste and improving flow in processes, while Six Sigma focuses on reducing variability and defects through statistical analysis. Lean Six Sigma combines both approaches to maximize efficiency and quality.
What is Process Improvement?
The term Process improvement refers to the systematic approach of identifying, analyzing, and enhancing existing processes within an organization to achieve better results, increase efficiency, and meet specific objectives. The goal of process improvement is to streamline workflows, reduce waste, enhance quality, and optimize overall performance.
What is a Process?
A process is a series of systematic and interrelated activities or steps undertaken to achieve a specific goal or outcome. In the context of business, manufacturing, or any organized activity, processes are the structured and repeatable sequences of tasks designed to produce a particular product, service, or result. Processes can be simple or complex, involving various stages, inputs, transformations, and outputs.
What is the DMAIC process in Lean Six Sigma?
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a structured, data-driven approach used in Lean Six Sigma to improve processes and solve problems.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma serves as a hybrid approach that combines the best of Six Sigma (quality and consistency) with the best of Lean (efficiency) to help organizations deliver customer value through efficient operations and quality standards, which results in creating higher quality products and services.
How does Lean Six Sigma work?
Lean Six Sigma works through a five-phase process known as DMAIC: Define the problem, Measure current performance, Analyze root causes, Improve processes, and Control future process performance to maintain improvements.
What are the principles of Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is built upon five key principles that guide organizations toward achieving excellence in efficiency and quality. These principles are: Focus on the Customer, Identify and Map the Value Stream, Create Flow, Establish Pull and Pursue Perfection
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma methodology?
Lean Six Sigma has many benefits to the organization, employee and customers. Some of the benefits include improved efficiency, decreased costs, increased quality and improved customer satisfaction.
What are the Steps in the Lean Six Sigma process?
The Lean Six Sigma process follows the framework of DMAIC. The phases include Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. These steps, organized within the DMAIC framework, provide a structured and data-driven approach to process improvement. Lean Six Sigma emphasizes continuous improvement, and after completing the Control phase, organizations often loop back to the Define phase to identify new improvement opportunities and initiate the cycle again.
What is Lean Six Sigma certification?
Lean Six Sigma certification can be achieved by completing a training program and passing an exam. There are five levels in Lean Six Sigma certification. these levels include: White Belt, Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt and Master Black Belt.
What is Lean Six Sigma Green Belt?
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification is an intermediate level training program that dives fully into the methodology of Lean Six Sigma and prepares you to work within process improvement teams. You will learn how to use various Six Sigma tools and techniques and apply them to real-world projects. Green Belt certification is intended for those with some prior experience or educational background in process improvement.
What is Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt?
Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt certification is an introductory level training program that will teach you the basic fundamentals of Lean Six Sigma and how it is applied to the DMAIC framework. Yellow Belt certification is for those new to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement.
What is Lean Six Sigma Black Belt?
Lean Six Sigma Black Belt certification is an advanced level training program that covers the complete methodology of Lean Six Sigma and prepares you to manage process improvement projects and teams. It is a high level statistics course that covers areas such as Design of Experiments and other statistical methods used in management of Six Sigma. Black Belt certification is intended for seasoned professionals and those in managerial positions or seeking to become leaders.
Is Lean Six Sigma certification worth it?
Lean Six Sigma certification is a valuable asset to any professional as it can help to increase salary, open new career opportunities in management and make one stand out from the competition.
How do I get certified in Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma certification is typically offered at various levels, such as Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt, and Master Black Belt. Certification programs are available through accredited training providers, and they usually involve coursework, exams, and project completion.
What are the most common Lean Six Sigma tools?
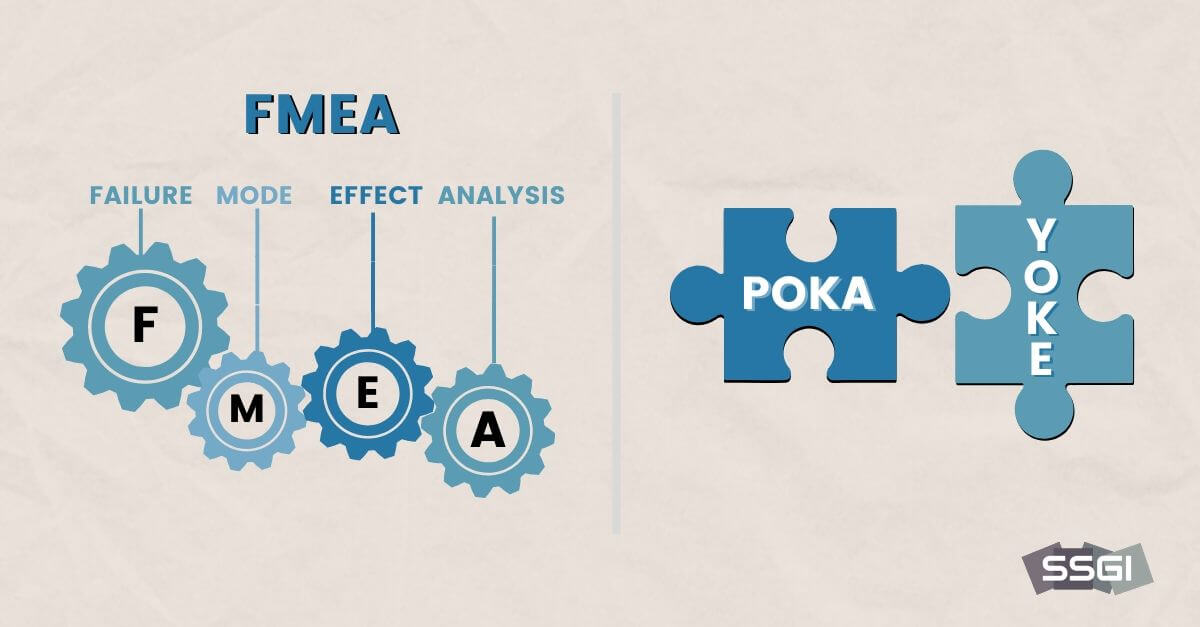
The most popular Lean Six Sigma tools and techniques include: SIPOC Diagrams, Voice of the Customer (VOC), Voice of the Process (VOP), Critical to Quality (CTQ), Value Stream Maps, Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ), Process Mean and Variation, Multi-Vari Charts, Sampling, Process Control, Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Poka-Yoke.
Who Uses Lean Six Sigma?
Everyone! Lean Six Sigma focuses on improving quality and consistency to deliver better products and services. From Healthcare and Manufacturing to Logistics and Retail, Lean Six Sigma is a valuable methodology used across all industries.
What types of projects are suitable for Lean Six Sigma?
Suitable projects for Lean Six Sigma are those that aim to improve process efficiency, reduce waste, decrease defects, enhance customer satisfaction, and lower costs. Projects can range from small process improvements to large-scale operational overhauls.
Get Started on Your Lean Six Sigma Process Improvement Journey Today
















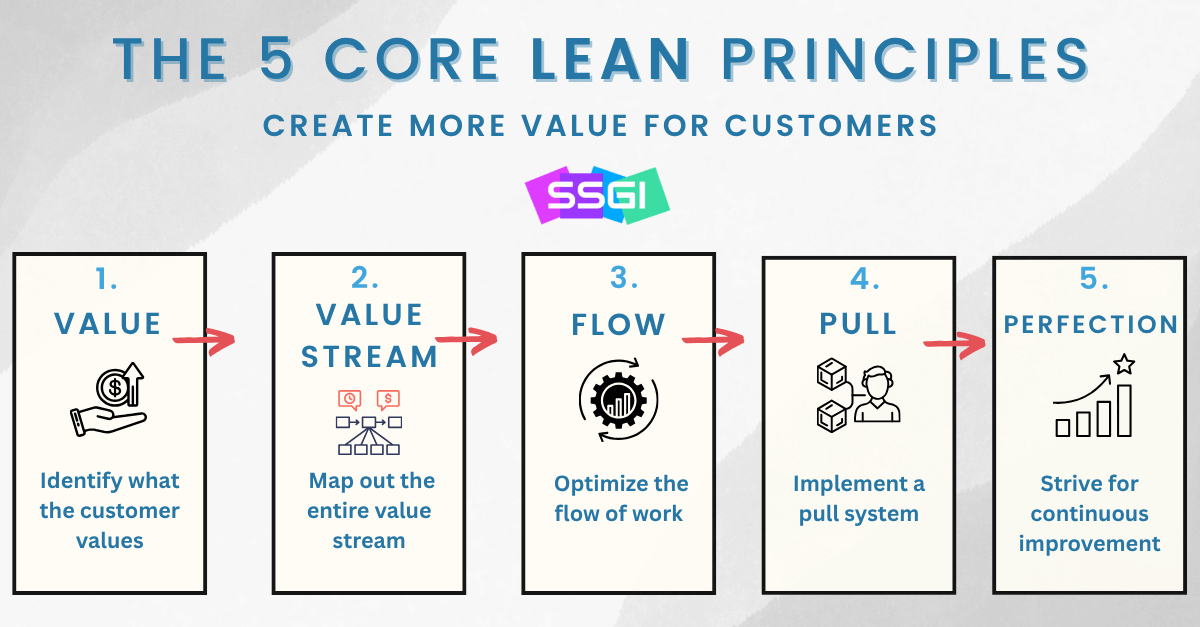 These five Lean principles form the foundation of every Lean system — helping organizations reduce waste, streamline processes, and improve customer value.
These five Lean principles form the foundation of every Lean system — helping organizations reduce waste, streamline processes, and improve customer value.

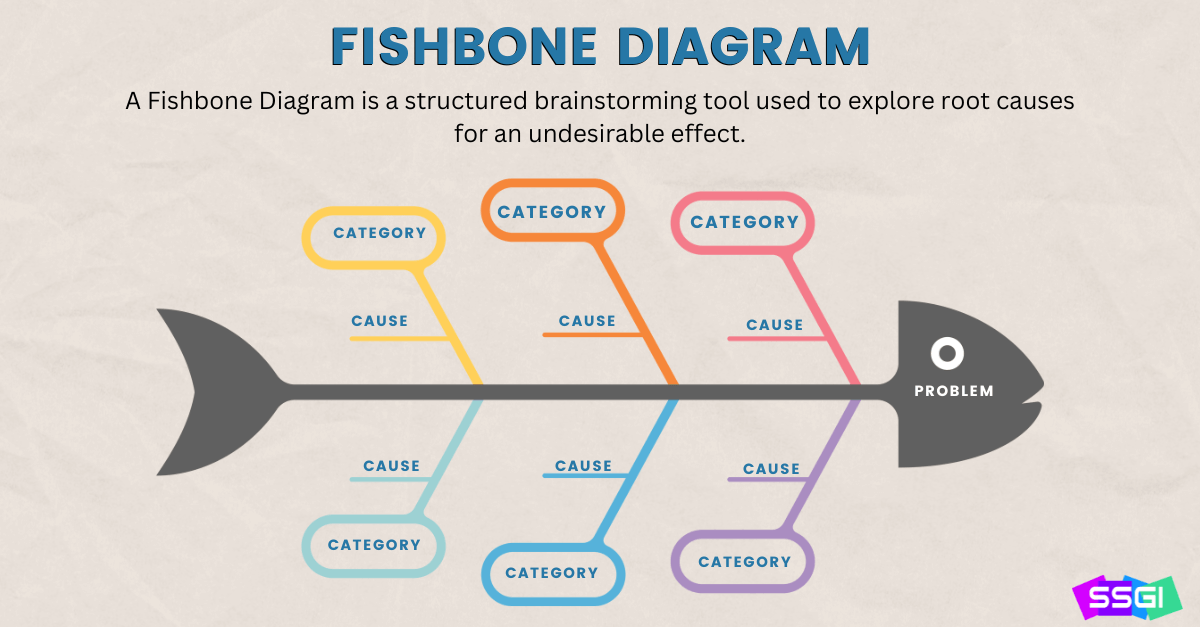
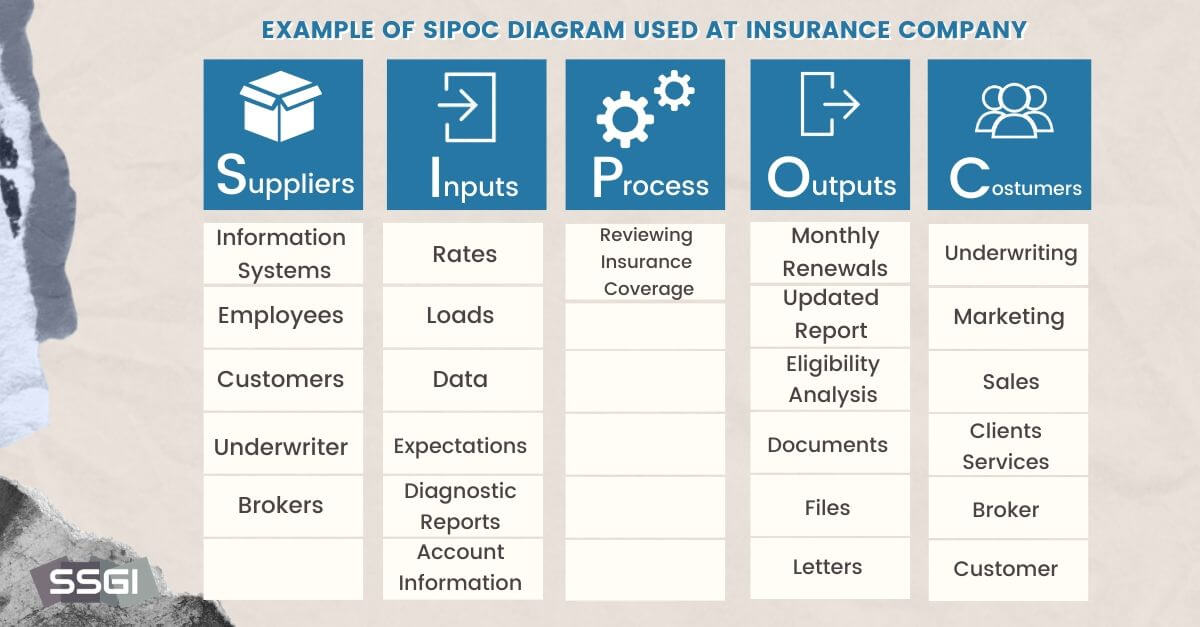
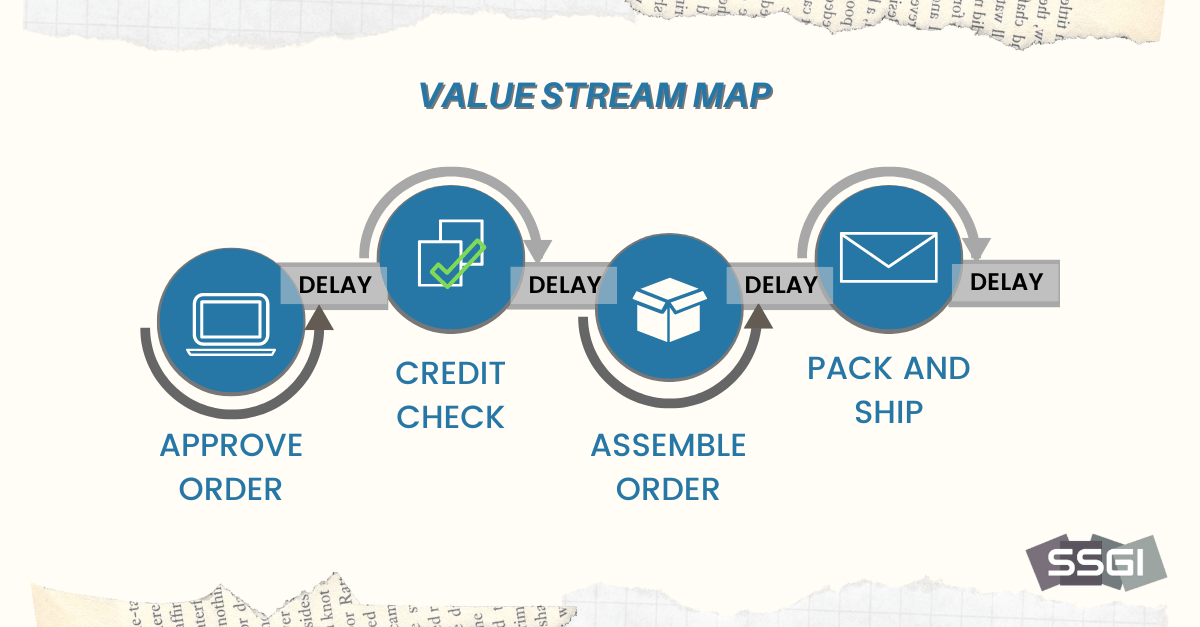

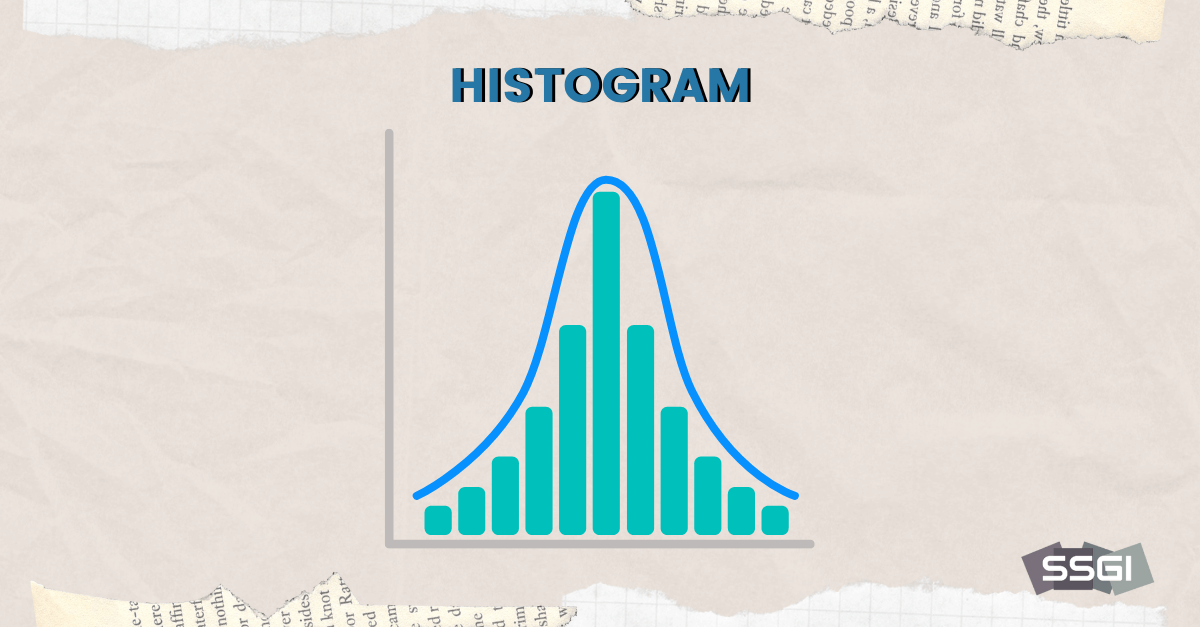
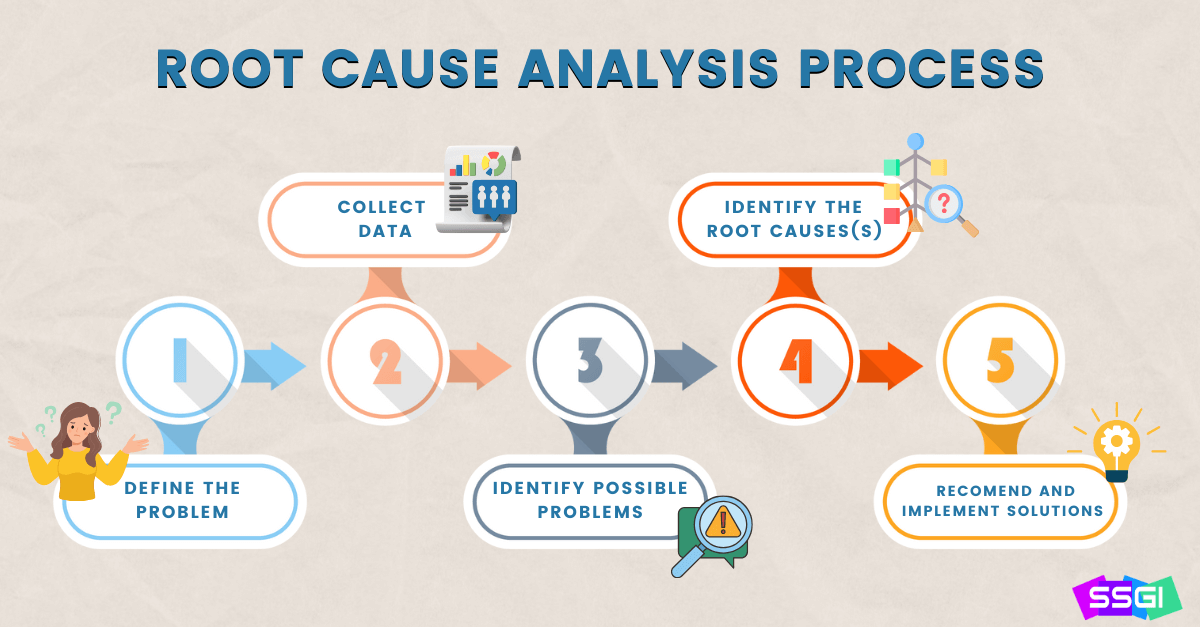 Root Cause Analysis is a systematic process to identify the underlying causes of problems, enabling effective solutions.
Root Cause Analysis is a systematic process to identify the underlying causes of problems, enabling effective solutions.