Typical responsibilities of a Six Sigma Green Belt in most organizations
A Six Sigma Green Belt is a trained problem-solver who leads and supports process improvement projects using Lean Six Sigma tools. Green Belts help organizations reduce waste, eliminate defects, and improve performance, often while balancing responsibilities in their primary role.
This page explains what Green Belts actually do, the tools they use, the duties they perform day to day, and how they contribute to improvement across industries.
👉 If you’re looking for the definition or meaning of the certification itself, see: What Is a Six Sigma Green Belt? →

Want to Learn More About Green Belt Certification?
Explore the full program details, curriculum, certification process, and pricing for SSGI’s industry-recognized Green Belt Certification.
View Green Belt Certification →Core Responsibilities of a Green Belt
Green Belts play a hands-on role in improvement. Their responsibilities typically include:
Leading small to mid-sized DMAIC projects
Improving cycle time, reducing errors, lowering costs, or enhancing customer satisfaction.Analyzing data to identify root causes
Using charts, Pareto analysis, mapping, and statistical tools to pinpoint process problems.Collaborating with cross-functional teams
Working with operations, finance, logistics, IT, manufacturing, and customer service teams.Implementing and validating improvements
Testing solutions, piloting changes, and measuring before-and-after performance.Sustaining improvements with control plans
Updating SOPs, creating visual controls, and monitoring metrics to ensure lasting results.Supporting Black Belt–led initiatives
Serving as analysts, team leaders, or data owners in larger enterprise-level projects.
Daily Duties of a Green Belt (What They Actually Do)
Green Belts divide their time between their regular job and project-related work. Daily tasks often include:
✔ Collecting data and reviewing process performance
✔ Running 5 Whys, fishbone diagrams, or mini root-cause workshops
✔ Mapping workflows using SIPOC or swimlane diagrams
✔ Meeting with team members to evaluate bottlenecks
✔ Updating dashboards or control charts
✔ Preparing presentations for sponsors or managers
✔ Working with frontline staff to test new processes
✔ Standardizing improvements by updating documentation
These duties shift depending on the industry, but all center on helping teams work faster, better, and more efficiently.
Tools & Methods Green Belts Use
Green Belts rely on structured problem-solving tools, including:
Six Sigma Tools
• DMAIC Methodology
• Measurement System Analysis (MSA)
• Control charts
• Hypothesis testing (basic)
• Pareto analysis
Lean Tools
• Waste identification
• 5S
• Kaizen
• Standard Work
Root Cause Tools
• Fishbone Diagram
• 5 Whys
• SIPOC
• Process mapping
Software Skills
• Excel
• Minitab (optional)
Real Examples of Green Belt Projects
Companies hire Green Belts because they deliver measurable results. Common projects include:
✔ Healthcare
• Reduce patient discharge time
• Decrease medication errors
• Streamline lab processing workflow
✔ Manufacturing
• Reduce defect rates
• Improve first-pass yield
• Shorten machine setup time
✔ Finance
• Reduce billing errors
• Improve loan processing turnaround
• Eliminate rework from manual reviews
✔ Logistics
• Optimize warehouse pick paths
• Improve on-time delivery
• Reduce inventory discrepancies
These examples show the versatility of the role across industries.

Where Green Belts Work (Industries)
Green Belts operate across industries such as:
• Healthcare
• Manufacturing
• Government
• Finance
• Supply Chain & Logistics
• Technology & IT
• Food & Beverage
Wherever processes exist, Green Belts add value.
Common Green Belt Job Titles
Lean Six Sigma Green Belts are qualified for a wide range of roles that involve process improvement, project leadership, and data-driven problem-solving. Common job titles include:
• Process Improvement Analyst
• Quality Analyst
• Operations Specialist
• Project Manager
• Business Analyst
• Continuous Improvement Manager
• Process Engineer
Want salary data for these roles? See Six Sigma salary and job role insights →
Skills Every Green Belt Needs to Succeed
High-performing Green Belts typically demonstrate:
• Analytical thinking
• Basic statistical literacy
• Problem-solving mindset
• Facilitation and communication skills
• Leadership and influence
• Collaboration across departments
• Ability to standardize and sustain improvements
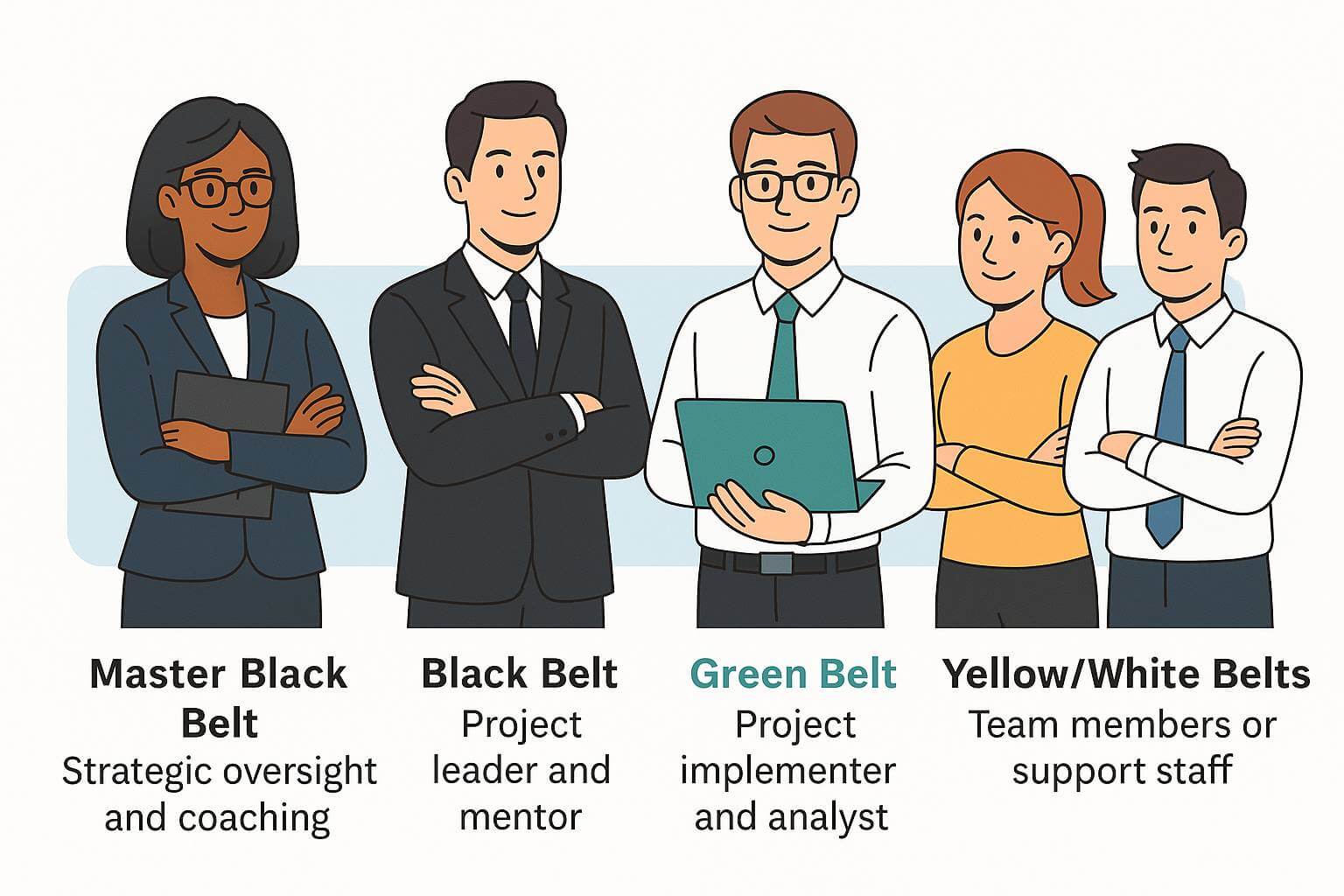
How Green Belts Fit Into a Six Sigma Team Structure
Six Sigma teams are typically structured like this:
Master Black Belt — strategic oversight
Black Belt — full-time project leader
Green Belt — project manager / analyst
Yellow Belt — project participant
Green Belts are essential contributors who bridge leadership strategy and frontline execution. Learn more about the different Six Sigma belt levels.

Career Advancement Opportunities After Green Belt
A Six Sigma Green Belt is often the foundation for broader leadership, specialization, and higher-impact roles.
Black Belt Certification
Lead cross-functional projects, mentor Green Belts, and drive major performance improvements across departments.
👉 Learn about Black Belt Certification →
Master Black Belt (MBB)
Provide enterprise-level strategy, coach leadership teams, and guide the organization’s continuous improvement roadmap.
Operational Excellence & CI Leadership Roles
Green Belts frequently move into roles such as Operational Excellence Manager, CI Lead, Quality Manager, Process Engineer, or Project Manager.
Cross-functional Leadership Pathways
The skills gained such as data analysis, problem-solving, and project leadership, also translate directly into advancement in operations, supply chain, healthcare administration, finance, and tech.
Green Belt is more than a certification, it’s a launching point for senior leadership, high-impact projects, and long-term career mobility.

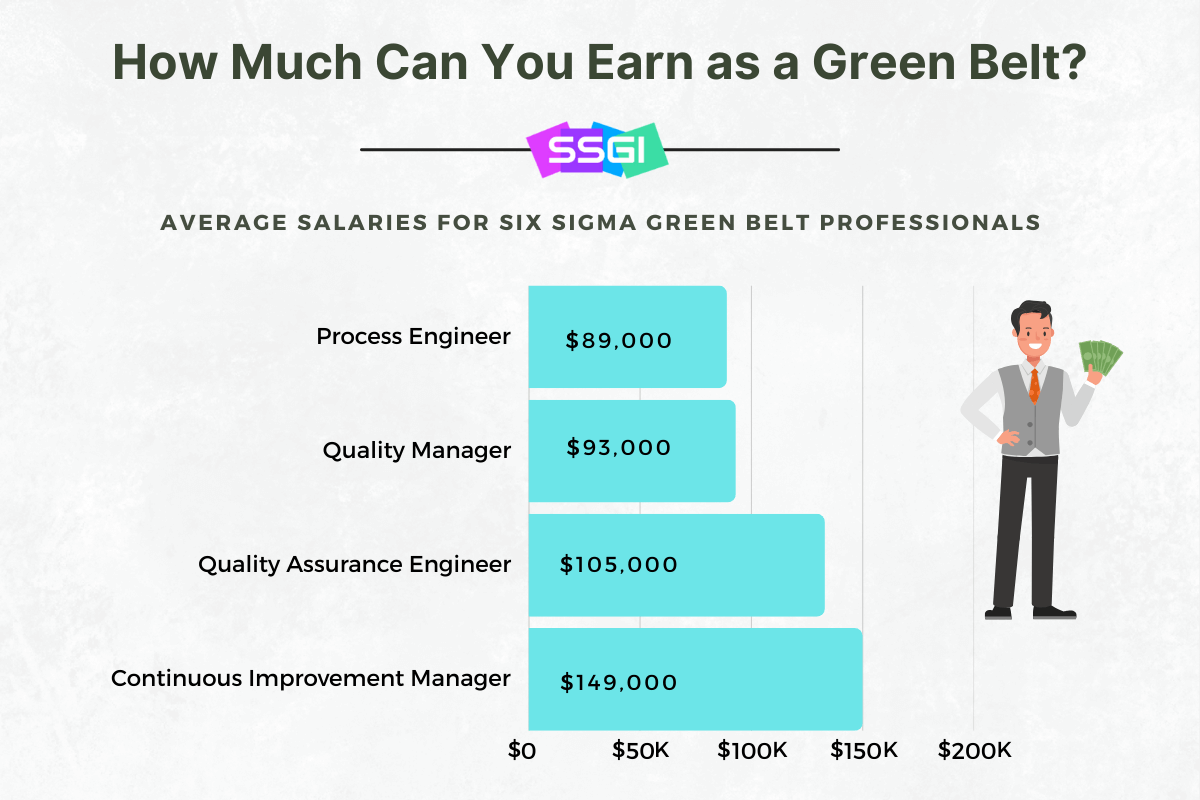
To compare salaries across industries and belt levels:
Salary Expectations for Green Belts
Earning a Six Sigma Green Belt can significantly increase your earning potential.
In the U.S., certified Green Belts typically earn $80,000 to $100,000 per year, with many professionals earning more as they gain experience or advance to Black Belt and leadership roles.
What influences Green Belt salary?
Industry – Healthcare, manufacturing, tech, and finance often pay above average
Experience – Salary increases as you lead more projects
Advanced certifications – Black Belt and MBB roles command higher pay
Job function – Analysts, project managers, CI roles earn at the top of the range
Is Green Belt Certification Worth It?
Yes, especially for professionals pursuing roles in operations, process improvement, analytics, project management, or quality.
Certification helps professionals develop structured problem-solving skills and advance into leadership roles.
Get Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certified
Ready to boost your career, improve processes, and lead projects with confidence? Our expert-developed Green Belt certification gives you the skills and recognition to stand out.
Learn More About Green Belt Certification →Frequently Asked Questions About Green Belt Certification
Have questions about Six Sigma Green Belt certification? Below you’ll find answers to the most common queries — including how it works, who it’s for, and what it can do for your career.
What does a Six Sigma Green Belt actually do?
A Green Belt leads small to medium-sized improvement projects, analyzes process data, identifies root causes, and implements solutions using the DMAIC framework.
Do Green Belts need to be full-time problem-solvers?
No. Most Green Belts balance project work with their regular job responsibilities.
What industries hire Green Belts?
Healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, finance, government, tech, and more.
What tools does a Green Belt use?
DMAIC, SIPOC, 5 Whys, control charts, fishbone diagrams, Pareto charts, and basic statistical analysis.
What is the career path after becoming a Green Belt?
Professionals typically advance to Black Belt, then Master Black Belt, with increased leadership responsibility and higher earning potential.
What is the role of a Green Belt in Six Sigma?
A Green Belt is responsible for leading small-to-medium improvement projects and supporting Black Belts on larger initiatives. They apply the DMAIC methodology, collect and analyze data, and contribute to operational efficiency and quality improvement.
Who should pursue Six Sigma Green Belt certification?
What is the difference between Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt?
Green Belts lead projects part-time and focus on applying Six Sigma tools within specific departments. Black Belts, on the other hand, manage large-scale projects full-time, use advanced statistical tools, and mentor Green Belts.
Is Six Sigma Green Belt certification required to work in quality?
While it’s not mandatory, Green Belt certification is highly preferred for roles in process improvement, operations, and quality. It demonstrates practical skills and a structured problem-solving mindset.
Do I need a Yellow Belt before Green Belt?
No. While having a Yellow Belt can be helpful, most Green Belt programs (including SSGI) are designed to be beginner-friendly and don’t require prior certification.
What salary can a certified Green Belt expect?
Certified Green Belts in the U.S. typically earn between $80,000 and $100,000 annually, depending on experience, role, and industry.
